- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Small Volume Injections›
- Caffeine Citrate Injection
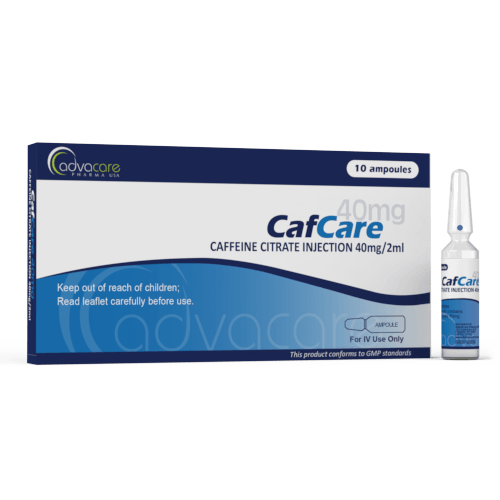
Caffeine Citrate Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Caffeine Citrate?
Active Ingredients: Caffeine Citrate
Caffeine Citrate Injection is a drug used for the short-term treatment of breathing problems in premature infants between 28 and 32 weeks of gestational age. Apnea of prematurity is caused by an underdeveloped breathing center. It may also be used to treat and prevent pulmonary complications in preterm infants.
Apnea of prematurity is a common medical condition caused by an underdeveloped breathing center. It occurs in over 50% of pre-term infants and nearly 100% of infants who weigh less than 1000g. This condition can increase a newborn's risk of developing chronic health conditions, and apnea episodes of over 1 minute may result in permanent disability or death. Intravenous caffeine citrate is commonly used to treat this condition, in addition to respiratory support and ongoing monitoring. It is an essential drug for many neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
Caffeine citrate is classified as a central nervous system stimulant. This compound is structurally similar to other methylxanthines such as theophylline and theobromine. Though the exact mechanism of action in regard to apnea of prematurity is unknown, methylxanthines are known to work by antagonizing adenosine A1 and A2 receptors. This works to stimulate the respiratory centers of the body, which increase respiratory rate, heart rate, cardiac contractility and output, and blood pressure. This action helps improve the supply of oxygen throughout the body and the brain.
Injections of caffeine citrate take effect within minutes and the compound is rapidly distributed to the brain. In premature infants, caffeine metabolism is limited and the elimination of caffeine is considerably slower than in adults. This is due to their immature hepatic or renal systems.
AdvaCare Pharma is a producer and exporter of Caffeine Citrate Injection. This medicine is produced in our GMP-certified facilities in China, India, and the USA. These facilities are regularly audited to ensure they comply with our high standards for health, safety, and environmental standards.
Why are we a leading Caffeine Citrate manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma, a US-owned pharmaceutical company, is a manufacturer of Caffeine Citrate Injection with GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities located worldwide. We conduct frequent GMP, third-party and internal facility inspections to ensure that our manufactured injectable treatments exceed the stringent requirements of importing countries and our distributors.
As a renown Caffeine Citrate manufacturer and global supplier of 120+ pharmaceutical injection products, our global reach extends to over 65 markets ensuring that pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs and government institutions receive the quality-assured treatments they need.
Uses
What is Caffeine Citrate used for?
It is used for the short-term treatment of apnea of prematurity in premature infants. It is sometimes used to treat and prevent bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in premature infants with a low birth weight.
How is Caffeine Citrate Injection used?
This medication is manufactured as a solution. It is intended to be slowly injected as an intravenous infusion over 10-30 minutes. Caffeine citrate should not be given intramuscularly, and it should be noted that bolus administration has been reported to cause sudden changes in blood pressure.
Treatment should be administered in a neonatal intensive care unit where adequate facilities for patient surveillance and monitoring are available.
How should unused Caffeine Citrate Injection be stored?
This product should be stored at a temperature below 25°C. It should be kept away from moisture or heat.
What dose should be given?
For apnea of prematurity in premature infants, the usual dose is 20-30mg/kg per dose, given by IV. After 24 hours, 5mg/kg per dose can be given, though higher doses may be necessary, such as continuing of apnea episodes. The dosage should be adjusted based on serum levels. It should be noted that dosing is expressed as caffeine citrate and that 20mg of caffeine citrate is equal to 10mg caffeine base.
Caffeine is clinically effective within 4 hours. If there is no response to the therapy, a second loading dose can be given.
Administration with caffeine citrate should continue until the patient has gone 5-7 days without a significant apnea episode. After discontinuing treatment, if apnea recurs, treatment can start with a half-loading dose or a maintenance dose. Treatment can generally be stopped at a gestational age of 37 weeks. At this time, the condition generally resolves itself.
Refer to a doctor or pharmacist for guidelines on dosage.
What are the signs of a Caffeine overdose in infants?
Reports have indicated that an overdose may occur if an infant's plasma caffeine levels are between 50mg/l and 350mg/l. Some signs of an overdose include tachycardia (increased heart rate), rigidity and tonic-clonic movements, tremors or non-purposeful jaw/lip movement, convulsions, stomach irritation, GI bleeding, vomiting, and fever. It should be noted that there have been no reported deaths due to caffeine overdose in premature infants.
In the event of overdosage, it is important to monitor blood levels of caffeine and provide supportive care as necessitated. Plasma potassium and glucose concentrations should be monitored in order to correct any hypokalemia and hyperglycemia. Seizures may be treated with intravenous anticonvulsants, such as diazepam or pentobarbital sodium.
What happens if a dose is missed?
As injections of caffeine citrate are typically administered in a hospital setting, it is unlikely for a dose to be missed.
Who can use Caffeine Citrate?
Injections of caffeine citrate are only indicated for pediatric patients. It can be given to premature infants, but dose adjustments and/or careful routine monitoring may be necessary for the following:
- premature neonates who are less than 28 weeks gestational age and/or with a bodyweight of less than 1000g, especially those who are being given parenteral nutrition.
- infants with liver or kidney impairment.
- infants experiencing seizures.
- infants with cardiac disease.
- infants receiving drugs that interfere with the metabolism of caffeine.
- infants who are breastfeeding from mothers who have consumed caffeine or taken medications like theophylline. It is known that caffeine is excreted into milk and readily crosses the placenta.
Can adults receive Caffeine Injection?
Caffeine Injections are not typically administered to adults. Caffeine citrate, the active ingredient within these injections, has been developed for the unique needs of premature infants. Adults do not typically suffer from apnea of prematurity, which is the primary indication of this medication. There has been some study of intravenous caffeine citrate in the treatment of acute migraine in adults; however, further investigation is necessary.
Is Caffeine Injection the same as consuming caffeinated beverages?
No, the compound used for Caffeine Injections differs from the caffeine commonly consumed in beverages. The caffeine found in beverages is most often caffeine anhydrous. The drug preparation for Caffeine Injection contains caffeine anhydrous in combination with citric acid monohydrate and sodium citrate dihydrate. The dose of caffeine citrate is half the dose of caffeine. That is, 10mg of caffeine citrate is equal to 5mg of caffeine base.
Other warnings and considerations
Baseline caffeine levels should be measured in infants who either have been previously treated with theophylline, or whose mothers may have consumed larger quantities of caffeine within the days before delivery.
At the recommended doses, frequent (more than weekly) monitoring of plasma levels is typically not necessary, except for at-risk patients. Due to the prolonged half-life in premature neonates, it is possible for caffeine to accumulate in the body. It is important to monitor these infants who are receiving extended therapy, and blood caffeine levels should be tested before each dose. When suspecting toxicity, testing should occur 2-4 hours after a caffeine dose.
As caffeine citrate may cause an increase in metabolism, there may be higher nutrition requirements during treatment. Additionally, fluid and electrolyte disturbances may occur due to diuresis and electrolyte loss due to the drug.
Caffeine citrate may exacerbate gastroesophageal reflux in infants suffering from this condition.
Animal studies have shown that caffeine is not associated with any mutagenic or oncogenic risks. At high dosages, some rodents have experienced convulsions, and at therapeutic doses, there have been some behavioral changes observed. Caffeine has shown some teratogenic potential and consequences on reproductivity in older animals, but these studies were not relevant for the target population.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Caffeine Citrate Injection.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- feeding intolerance
- skin rash
- hyperglycemia (high blood sugar)
- inflammation at the site of injection
- tachycardia
Some rare, but serious adverse effects that may occur include:
- hypersensitivity responses
- necrotizing enterocolitis
- sepsis
- hemorrhage
- renal failure
- retinopathy of prematurity
- pulmonary edema
Seek medical attention if the infant has:
- continued sleep apnea
- increased heart rate
- restlessness, jitteriness, or shaking
- increased diaper-wetting
- abdominal distension
- vomiting
- bloody stools
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or any new symptoms appear, please call your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Caffeine Citrate Injection if: • the infant is allergic or hypersensitive to any of the ingredients.
This medication may not be suitable for patients with certain conditions, including:
- renal or hepatic impairment
- heart problems or cardiovascular disease
- seizures
There are many drugs that are known to have the potential to interact with caffeine citrate. Some medications that may need to be avoided during treatment with include alosetron, aminophylline, theophylline, bendamustine, methotrexate, ephedra, furosemide, midodrine, pirfenidone, and tizanidine. Certain types of ACE inhibitors, angiotensin blockers, adrenergic agents/blockers, antibiotics, antidepressants, and warfarin may also need careful consideration. This is not a complete list of possible drug interactions. Caffeine citrate is also contraindicated with fezolinetant.
References
Caffeine Citrate for the Treatment of Apnea of Prematurity: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
The objective of this research was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of caffeine citrate for the treatment of apnea of prematurity.
This is a multicenter, parallel, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with an open-label rescue that included nine neonatal intensive care units and 85 infants, 28–32 weeks postconception and 24 hours or more after birth who had six or more apnea episodes within 24 hours.
Caffeine citrate 10mg/kg (as caffeine base) administered intravenously, followed by 2.5mg/kg/day orally or intravenously, or placebo, for up to 10 days.
There was a 50% or greater reduction in apnea episodes and elimination of apnea. Caffeine citrate demonstrated significant efficacy compared to placebo in reducing apnea episodes by at least 50% within 6 days (p < 0.05) and showed a trend towards statistical significance within 3 days (p < 0.10). It was more effective than placebo in completely eliminating apnea within 5 days (p < 0.05) and approached significance within 2 days (p < 0.10). The proportion of infants experiencing a 50% reduction in apnea episodes or complete elimination of apnea for 7–10 days was significantly higher in the caffeine-citrate group compared to the placebo group.
The conclusion of this study is that caffeine citrate is safe and effective for treating apnea of prematurity in infants 28–32 weeks postconception.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.