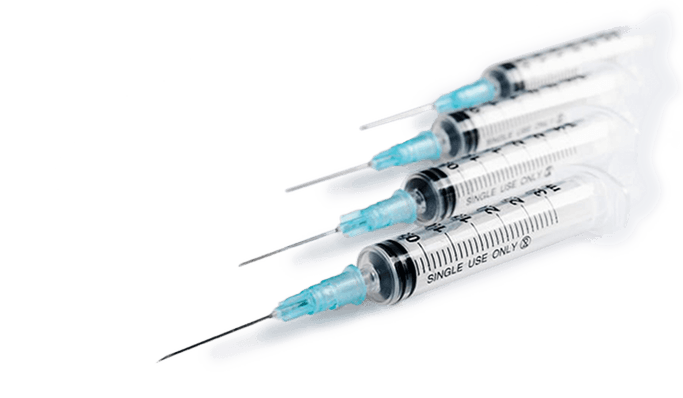
What is the meaning of Injection Instruments?
Injection Instruments are devices used to administer medication or fluids directly into the body. They include syringes, needles, infusion sets, and IV cannulas. Injection instruments are common in hospitals, clinics, and healthcare settings for administering vaccines and drugs, delivering fluids, and more.
Injection instruments come in different sizes and shapes, with different features depending on their intended use. For instance, needles vary in length and thickness depending on where they are meant to be inserted into the body. Infusion sets include tubing and needles that can be inserted into veins or arteries to provide a continuous flow of medication or fluids. IV cannulas are small, flexible tubes that can be inserted into a vein to deliver medication or fluids.
The evolution of injection instruments has been influenced by advances in technology and feedback from medical professionals. Modern designs emphasize patient comfort, precision in delivery, and user-friendly interfaces. For example, auto-injectors have been developed to allow patients with conditions like diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis to self-administer medication with minimal discomfort and hassle. Furthermore, innovations like safety-engineered needles are designed to reduce the risk of needlestick injuries, highlighting the industry's commitment to safety and continuous improvement.
The use of injection instruments requires meticulous attention to detail and rigorous adherence to best practices. Proper training ensures that healthcare professionals can accurately dose and administer medications, minimizing the risk of overdose or underdose. Furthermore, understanding and consistently applying infection control measures, like hand hygiene and proper instrument disposal, protect both the patient and the healthcare provider. Emphasizing needle safety not only prevents unintentional injuries but also reduces the potential transmission of bloodborne pathogens.