- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Powder for Injection›
- Ceftriaxone Sodium for Injection
Ceftriaxone Sodium for Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Ceftriaxone Sodium?
Active Ingredients: Ceftriaxone Sodium
Ceftriaxone Sodium for Injection is an antibiotic drug that is used to treat severe or life-threatening bacterial infections. It is indicated for the treatment of acute bacterial otitis media, infections of the lower respiratory tract, skin and skin structures, bone and joint, and urinary tract.
Ceftriaxone is also used to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, intra-abdominal infections, gonorrhea, meningitis, and septicemia caused by susceptible microorganisms. This medication may be used to prevent infection in patients undergoing certain surgeries.
Ceftriaxone belongs to the family of antibiotics known as cephalosporins. It is a broad-spectrum bactericidal agent that works by inhibiting the synthesis of the main component of bacterial cell walls. Ceftriaxone’s beta-lactam functional group binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) in the bacterial wall and prevents them from synthesizing peptidoglycan, which inhibits cell division and cell wall synthesis and results in bacterial death.
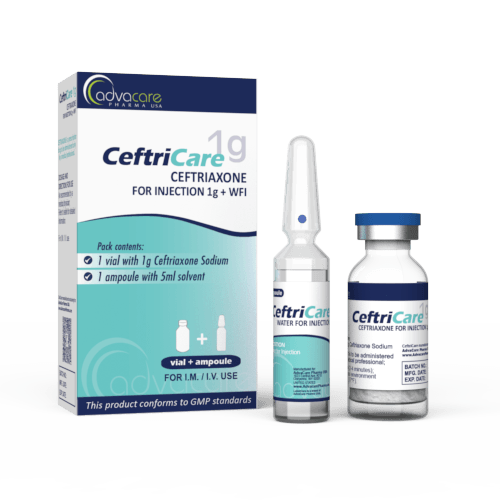
This formulation of Ceftriaxone Sodium has been manufactured as a fine powder for reconstitution, which is available packaged as a box of 10 or 50 vials. AdvaCare Pharma also produces a range of convenient combination packs with Water for Injection, 1% Lidocaine HCl, or both Water for Injection and 1% Lidocaine HCl. Water for Injection is a drug diluent in a single-dose container, which is intended for intravenous (IV) administration. Lidocaine is a corticosteroid that may be used to minimize the pain caused by an intramuscular (IM) injection of this antibiotic. It is important to note that lidocaine is intended for IM injection and cannot be administered via the IV route.
Ceftriaxone Sodium for Injection is produced and exported by AdvaCare Pharma. This medicine is manufactured in our facilities in China, India, and the USA. These production factories are GMP-certified and are regularly inspected to ensure they meet health, safety, and environmental standards.
Why choose us as your Ceftriaxone manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma, a US-owned pharmaceutical company, is a manufacturer of Ceftriaxone for Injection with GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities located worldwide. We conduct frequent GMP, third-party and internal facility inspections to ensure that our manufactured injectable treatments exceed the stringent requirements of importing countries and our distributors.
As a renown Ceftriaxone manufacturer and global supplier of 120+ pharmaceutical injection products, our global reach extends to over 65 markets ensuring that pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs and government institutions receive the quality-assured treatments they need.
Uses
What is Ceftriaxone Sodium used for?
It is used to treat various types of bacterial infections, such as:
This drug is also used to prevent infection in patients undergoing certain surgeries or procedures.
How is Ceftriaxone Sodium for Injection used?
This medication is manufactured as a powder, which is to be mixed into a solution. The reconstituted solution is intended for injection via the intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) route.
Injections should only be prepared when they are ready to be used. Ceftriaxone should not be mixed with other antibiotics or any diluent that contains calcium.
When administering ceftriaxone via IM injection, it can be dissolved in lidocaine, which is used as an anesthetic to reduce the pain. If the reconstituted solution contains lidocaine, it should not be administered via IV injection. If ceftriaxone is intended for injection by IV, it should be mixed with Water for Injection.
This medication should be taken for the full prescribed length of time, even if symptoms improve. Skipping doses or discontinuing treatment prematurely increases the risk of developing infections that are resistant to present and subsequent treatments.
What dose should be given?
Adults Recommended dosage guidelines may vary depending on medical condition:
- For the treatment of ear, lower respiratory tract, skin, urinary tract, bone and joint, and intra-abdominal infections, the recommended dosage is 1-2g/day via IV or IM. Daily dosages should not exceed 4g.
- For the treatment of meningitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and sepsis, the recommended dosage is 1-2g/day via IV or IM. Daily dosages should not exceed 4g.
- For the treatment of bacterial sexually transmitted infections, the recommended treatment is a single dose of 250mg via IM. Daily dosages should not exceed 4g.
- For the prevention of infection during surgery, the recommended treatment is a single dose of 1g via IV, given 30 to 120 minutes before surgery. Daily dosages should not exceed 4g.
Children (0 - 17 years) Recommended dosage for children may vary based on different medical conditions:
- For the treatment of ear, lower respiratory tract, skin, urinary tract, bone and joint, and intra-abdominal infections, the recommended dosage is 50-75mg/kg/day via IV or IM. Daily dosages should not exceed 2g.
- For the treatment of meningitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and sepsis, the recommended dosage is 50-75mg/kg/day via IV or IM. Daily dosages should not exceed 2g.
- For the treatment of bacterial sexually transmitted infections in children weighing up to 45kg, the recommended treatment is a single dose of 25-50mg via IV or IM. Dosages should not exceed 125mg. Children weighing more than 45kg can receive the adult dose.
- For the prevention of infection during surgery, the recommended treatment is a single dose of 50-75mg/kg via IV, given 30 to 120 minutes before surgery. Daily dosages should not exceed 2g.
Treatments not given as single doses should last 4 to 10 days and for at least 10 days when treating infections due to Streptococcus pyogenes. In adults and children (≥ 1 month), IV infusions should be administered over 30 minutes. In neonates, infusions should be administered over 60 minutes to reduce the risk of bilirubin encephalopathy.
The exact dosage is based on the severity of the infections, age, sex, and weight. Refer to a doctor or pharmacist for more guidelines on dosage.
Who can use Ceftriaxone?
Ceftriaxone can be administered to adults and children. Special caution is advised for specific groups of patients.
Pregnant Animal studies have not found evidence of fetal harm associated with ceftriaxone administration at doses 20 times the maximum recommended human dose (MHRD). Studies in pregnant people are inadequate to rule out risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes with ceftriaxone use during pregnancy.
Maternal gonorrhea may be associated with preterm birth, low birth weight, chorioamnionitis, intrauterine growth restriction, small for gestational age, and premature rupture of membranes. Gonorrhea transmitted to neonates during delivery may cause infant blindness, joint infections, and bloodstream infections. In cases of maternal gonorrhea, the benefits of ceftriaxone may outweigh the potential risks and the women are less likely to experience the signs of the disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests this antibiotic for treating maternal gonorrhea.
Nursing Ceftriaxone is excreted in human milk in small amounts. The effects on nursing infants are unknown. Caution should be exercised when administering ceftriaxone to nursing patients.
Pediatric Ceftriaxone use is contraindicated in hyperbilirubinemic neonates, especially premature neonates, and those receiving IV infusions containing calcium.
Geriatric Clinical studies and reported experiences of ceftriaxone treatment have not observed differences between older adults (≥ 65 years) and younger adults (< 65 years). Ceftriaxone is primarily excreted renally. Due to age-related decreases in renal function, dosages should be adjusted based on creatinine clearance, and renal function monitoring is encouraged.
Other warnings
In patients with hepatic insufficiency, dosage adjustments may not be necessary.
In patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency, dosage reductions may be necessary.
In patients with both hepatic and renal dysfunction, dosages of ceftriaxone should not exceed 2g/day, and close observation is recommended.
Serious and potentially fatal hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with ceftriaxone and other beta-lactam agent use. In cases of severe cross-reactivity reactions, ceftriaxone should be discontinued immediately.
Ceftriaxone can precipitate out of solution if mixed with calcium-containing diluents and when administered through the same IV line. Mixing and simultaneous administration via IV should be avoided.
Ceftriaxone-calcium precipitates have been observed on the sonographies of gallbladders and urinary tracts of patients receiving ceftriaxone. Patients may be asymptomatic or develop symptoms of gallbladder or renal disease. If patients develop signs and symptoms of organ dysfunction or precipitates, ceftriaxone should be discontinued immediately, and symptoms are typically reversible upon treatment cessation.
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibiotic agents, including ceftriaxone, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibiotics alters the flora of the colon, which can lead to overgrowth of C. difficile. Certain strains of C. difficile can cause increased morbidity and mortality. Patients presenting with diarrhea up to weeks or months after the completion of ceftriaxone treatment should be monitored for CDAD. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not intended to treat C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Administering ceftriaxone in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide any clinical benefit and increases the risk of developing drug-resistant bacterial infections.
Cephalosporins, including ceftriaxone, may be associated with an increase in prothrombin time. This risk is increased in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency, poor nutritional state, those receiving prolonged antimicrobial therapy, and those who are taking anticoagulants. Prothrombin time should be monitored in such patients, and supplemental vitamin K may be administered, if needed.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Ceftriaxone Sodium for Injection.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- a hard lump where the injection was given
- pain at the injection site when injected IM
- vomiting
- upset stomach
- headache
- dizziness
- overactive reflexes
- sweating
Serious side effects may occur. Seek medical attention if the following develop:
- signs of an allergic reaction
- signs of a liver or gallbladder problem
- signs of a new infection
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or you notice any other symptoms, please call your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Ceftriaxone Sodium for Injection if:
- You are hypersensitive to any of the ingredients.
- You have renal or hepatic impairment.
- You have gallbladder pseudolithiasis, pancreatitis, or acute renal failure.
References
A randomised, multicentre study of ceftriaxone versus standard therapy in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections
This study examined the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of intravenous ceftriaxone compared to the standard antibiotic treatment (STD) for lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI). Out of 100 patients, 52 received CTX, while 48 received STD. Seventy patients had pneumonia, while twenty-nine had severe chronic bronchitis, and one patient did not have a confirmed LRTI.
The most isolated pathogens from the sputum and blood were Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. CTX patients had 15 15-day average duration of hospitalization while STD patients had a 15.9 average duration of hospitalization.
The improvement and overall cure rate was 47 (90%) for patients who receive CTX, while it was 37 (77%) for patients receiving STD. Eradication of pathogens was 84% in the CTX patients and 76% in STD patients.
The conclusion of this study is ceftriaxone has similar efficacy as STD but it can reduce the treatment costs and it is highly recommended for respiratory diseases.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.