- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Small Volume Injections›
- Magnesium Injection
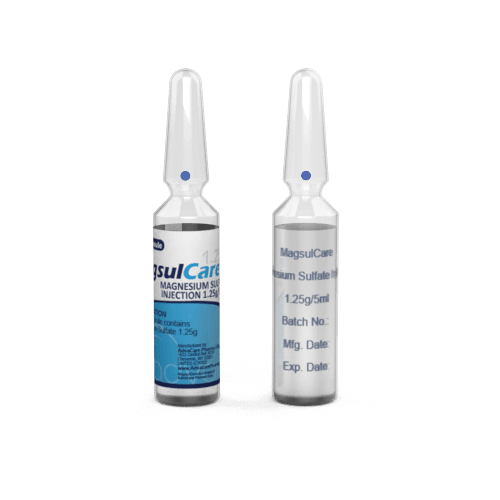
Magnesium Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Magnesium Sulfate?
Active Ingredients: Magnesium Sulfate
Magnesium Sulfate Injection is used to treat hypomagnesemia (low magnesium levels) associated with illness or treatments with certain medicines. This medication can also be used to prevent seizures in children with acute nephritis or women with preeclampsia, eclampsia, or toxemia of pregnancy.
Magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄) is a chemical compound consisting of magnesium, sulfur, and oxygen. Magnesium is a mineral that is essential for many bodily functions, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, metabolism, maintaining regular heartbeats, and regulating blood pressure. It is also a structural component of bones and teeth.
Parenteral magnesium sulfate is typically administered as an electrolyte replenisher or for its anticonvulsant properties. As an anticonvulsant, it works by depressing the central nervous system and blocking peripheral neuromuscular transmission, which helps prevent seizures. Magnesium sulfate is immediately absorbed when administered intravenously and within an hour when given intramuscularly.
AdvaCare Pharma's Magnesium Sulfate Injections are manufactured in GMP-certified facilities located in China, India, and the USA. We routinely inspect our production facilities to ensure our products meet health, safety, and environmental standards. We offer a wide range of high-quality and cost-effective medications that are available for distribution.
Why are we a leading Magnesium Sulfate manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma, a US-owned pharmaceutical company, is a manufacturer of Magnesium Sulfate Injection with GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities located worldwide. We conduct frequent GMP, third-party and internal facility inspections to ensure that our manufactured injectable treatments exceed the stringent requirements of importing countries and our distributors.
As a renown Magnesium Sulfate manufacturer and global supplier of 120+ pharmaceutical injection products, our global reach extends to over 65 markets ensuring that pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs and government institutions receive the quality-assured treatments they need.
Uses
What is Magnesium Sulfate used for?
It is used to treat low levels of magnesium in the blood. It is also used to prevent seizures in pregnant women with preeclampsia, eclampsia, or toxemia of pregnancy and children with acute nephritis.
How are Magnesium Sulfate Injections used?
This medication is manufactured as a solution to be injected into a muscle or a vein. It should be administered by a healthcare professional in a hospital or clinic setting.
What dose should be given?
Adult Dosing For the treatment of symptomatic hypomagnesemia, the usual dose is as follows:
- hemodynamically stable: 4-8g given IV over 12-24 hours, as needed. The starting dose should be 1-2g, given once over 5-60 minutes by IV. The dose can be adjusted based on serum magnesium levels.
- hemodynamically unstable: 1-2g given IV over 2-15 minutes. If necessary, this dose may be followed with 3-20mg per minute, IV.
For the treatment of asymptomatic hypomagnesemia, the usual dose is as follows:
- plasma Mg < 1mg/dL: 4-8g given IV over 12-24 hours. Alternatively, up to 250mg/kg per dose can be administered IM within 4 hours.
- plasma Mg 1-1.5mg/dL: 2-4g given IV over 4-12 hours.
- plasma Mg 1.6-1.9mg/dL: 1-2g given IV over 1-2 hours. Alternatively, 1g can be administered IM every 6 hours for up to 4 doses.
For seizures associated with preeclampsia or eclampsia, the usual dose is 1-2g/h IV for at least 24 hours. The starting dose is 4-6g, given once by IV. The maximum dosage is 40g per 24 hours for 5-7 days. If there is no IV access available, 5g can be administered to IM into each buttock, followed by 5g to alternative buttocks every 4 hours as needed.
For tocolysis, the usual dose is 2-4g per hour IV, given for 12-24 hours. The starting dose should be 4-6g given one by IV. The maximum length of treatment is 5-7 days.
For ventricular arrhythmia, the usual dose is 3-20mg per minute, given IV for 5-48 hours. The starting dose is 2-6g, given once IV.
For torsades de pointes, the usual dose is as follows:
- without cardiac arrest: 1-2g, given IV once over 15 minutes. If necessary, this can be followed with 3-20mg per minute, IV.
- with cardiac arrest: 1-2g, given IV once over 1-2 minutes. If necessary, this can be followed with 3-20mg per minute, IV.
For severe asthma exacerbation (adjunct treatment), the usual dose is 2g, given once IV.
Renal Dosing for Adults For severely impaired function in patients experiencing seizures (associated with preeclampsia or eclampsia), the maximum dosage is 20g per 48 hours. For all other indications, the usual amount should be decreased, though the amount is not defined.
Pediatric Dosing For symptomatic hypomagnesemia, the usual dose is as follows:
- neonates: 25-50mg/kg per dose, given IV every 8-12 hours, for 2-3 times.
- infants/children: 25-50mg/kg per dose, given IV every 6 hours, for 3-4 times.
For acute nephritis, the usual dose is 100mg/kg, given IM every 4-6 hours, as needed. Alternatively, 20-40mg/kg can be given IM as needed. For severe cases, 100-200mg/kg should be administered by IV as a 1-3% solution. The entire dose should be given within 1 hour and the first half within the first 15-20 minutes.
For ventricular arrhythmias due to post-cardiopulmonary bypass (prophylaxis/ treatment), the usual dose is 25-50mg/kg given one IV. The maximum dosage is 2g per dose.
For torsades de pointes, the usual dose is 25-50mg/kg, given once IV/IO, as needed. The maximum dosage is 2g.
For severe asthma exacerbation (adjunct treatment), the usual dose for children older than 2 years old is 25-50mg/kg per dose, given once IV over 10-20 minutes. The maximum dosage is 2g.
For children with renal impairment, the adult dosing guidance should be considered before administering magnesium injections.
Refer to a doctor for guidelines on dosage. The exact dosage is based on medical condition, response to the treatment, age, and weight.
Who can use magnesium?
Magnesium Injections can be administered to adults and children, but caution is advised for specific groups of patients.
Pregnant For life-threatening emergencies, magnesium sulfate may be administered to pregnant women. The benefits must be weighed against the risks when considering prolonged treatment of over 5-7 days. Limited human data suggests that prolonged use may lead to fetal hypocalcemia, hypermagnesemia, or congenital rickets. This drug should not be administered during the 2 hours before delivery for women with toxemia during pregnancy.
Breastfeeding Parenteral magnesium sulfate is considered safe for use in breastfeeding women. Based on limited human data, there may be a possible risk of transient delayed milk production.
Geriatric As renal impairment is common in elderly patients, reduced dosages may be necessary. For those with severe impairment, the maximum dosage is 20g in 48 hours. It is recommended to monitor serum magnesium during treatment.
Other warnings
During parenteral therapy with magnesium sulfate, it is recommended to monitor renal function, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and deep tendon reflex.
For patients with renal impairment, the renal excretory capacity should not be exceeded. In these patients, urine output should be monitored during treatment.
This drug should be cautiously administered to patients under digitoxin treatment. Extreme caution is necessary for those with myasthenia gravis or other neuromuscular diseases.
Dosing may need to be adjusted for patients also being treated with inhalation anesthetics or barbiturates, narcotics, or other hypnotics.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Magnesium Sulfate Injection.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- redness at the injection site
- drowsiness
- flushing of the skin
- excessive sweating
- vision changes
- temporary hypotension
- impaired cardiac function
- slowed reflexes
- low levels of calcium (hypocalcemia) or phosphate (hypophosphatemia)
- high levels of magnesium (hypermagnesemia)
Severe reactions may include:
- allergic reactions
- depressed cardiac function
- cardiovascular collapse
- respiratory paralysis
- hypothermia
- pulmonary edema
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or you notice any other symptoms, please call your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Magnesium Sulfate Injection if:
- You are allergic to any of the ingredients.
- You have a severe irregular heartbeat, heart block, or myocardial damage.
- You are in a diabetic coma.
- You have hypermagnesemia or hypercalcemia.
- You are pregnant and expect to deliver the baby within 2 hours.
Before treatment, consult your doctor regarding any medications you are taking to address potential drug interactions.Some drugs that are known to interact with magnesium sulfate include tetracycline antibiotics (such as demeclocycline, doxycycline, minocycline, oxytetracycline, tetracycline), calcium channel blockers, CNS depressants, digitalis, baloxavir marboxil, calcitriol, and doxercalciferol. This is not a complete list.
This medication may not be suitable for people with certain conditions, so it is important to consult with a doctor if you have any health conditions. Special considerations or alternative dosing and monitoring may be necessary for patients with heart problems, liver or kidney impairment, or breathing problems.
This solution of magnesium sulfate may contain aluminum. It is crucial to monitor patients with liver dysfunction, as their aluminum levels could reach toxicity during prolonged treatment. Special caution should be taken for premature neonates.
References
A randomised study of magnesium sulphate as an adjuvant to intrathecal bupivacaine in patients with mild preeclampsia undergoing caesarean section
This study evaluates the efficacy of magnesium in women with mild preeclampsia. It included 60 women with mild preeclampsia who underwent a cesarean section in a prospective double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Some of the patients received spinal anesthesia with a combination of either 0.1mL of 0.9% sodium chloride (control group) or 0.1mL of 50% magnesium sulphate (50mg) (magnesium group).
The magnesium group exhibited slower onset for both sensory and motor block. The duration of spinal anesthesia (229.3 vs. 187.7 minutes) and motor block (200 vs. 175.3 minutes) were prolonged in the magnesium group. Following surgery, there was a reduction in diclofenac requirement over 24 hours in the magnesium group compared to the control (147.5 vs. 182.5mg, p=0.02).
The conclusion is that women with mild preeclampsia undergoing cesarean delivery can benefit from the addition of magnesium sulfate 50mg to the intrathecal combination of bupivacaine and fentanyl. Magnesium can also prolong the duration of analgesia and reduce postoperative analgesic requirements without additional side effects.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.