- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Small Volume Injections›
- Atropine Injection
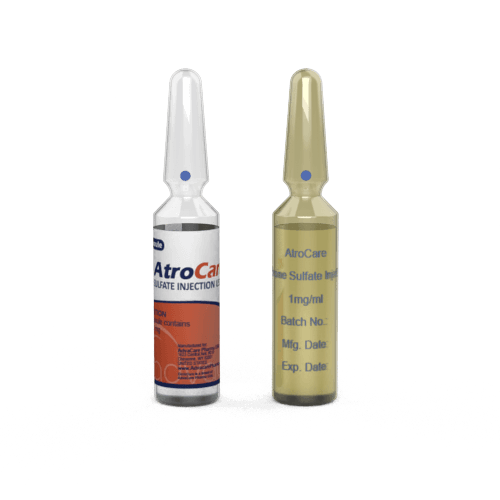
Atropine Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Atropine?
Active Ingredients: Atropine Sulfate
Atropine Injection is a drug used before anesthesia to decrease saliva and other mucus secretions. It is also used as an emergency treatment for bradycardia, nerve gas poisoning, and mushroom poisoning. In the treatment of Parkinson's disease, atropine can relieve symptoms of rigidity, tremor, salivation, and sweating.
Atropine is a naturally occurring substance found in deadly nightshade, Jimson weed, and mandrake. It is generally considered to be an anticholinergic or anti-parasympathetic drug. Atropine also displays antimuscarinic properties. This drug works by inhibiting smooth muscles and glands, and it also relaxes the GI tract and decreases the activity of the urinary tract.
Atropine acts as an antimuscarinic agent by antagonizing the muscarine-like effects of acetylcholine and other choline esters. This drug inhibits the muscarinic actions of acetylcholine. Like other antimuscarinic agents, the primary action of atropine involves competitive or surmountable antagonism. This antagonistic effect can be overcome by elevating the concentration of acetylcholine at the receptor sites of the effector organ.
The receptors affected by atropine are peripheral structures that are either stimulated or inhibited by muscarine, such as exocrine glands and smooth and cardiac muscles. While atropine can also inhibit responses to postganglionic cholinergic nerve stimulation, this occurs less readily compared to responses to injected (exogenous) choline esters.
This drug disappears rapidly from the blood when administered parenterally and it is widely distributed to the whole body. In humans, exercise prior to and after the Atropine administration can increase the absorption of Atropine due to the increased perfusion in the muscle. After intravenous administration (0.5 to 4mg) of this drug, the plasma protein binding is about 44%. It is saturable in the 2-20μg/mL concentration range. This drug crosses the placental barrier and enters the fetal circulation. When given during pregnancy, it is not found in the amniotic fluid. The elimination of the drug is by enzymatic hydrolysis in the liver. Around 13-50% is excreted unchanged in urine. There are traces of this drug in the human milk. The metabolites released by Atropine are noratropine, atropin-n-oxide, tropine, and tropic acid. The effects of this drug can be inhibited by exposure to organophosphate pesticides.
The elimination half-life of Atropine is doubled in children under two years and patients of 65 years and older. In healthy individuals, 29% of the drug is eliminated through urine, and 15% is eliminated as unidentified metabolites.
This drug is also available as Atropine Sulfate Injection (used in the veterinary medicine) and Atropine Sulfate Eye Drops.
AdvaCare Pharma is a manufacturer and supplier of Atropine Injections. We offer a wide range of high-quality and cost-effective medical supplies that are available for distribution. Our medications are produced in our GMP-certified facilities in China, India, and the USA.
Why are we a leading Atropine manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma, a US-owned pharmaceutical company, is a manufacturer of Atropine Injection with GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities located worldwide. We conduct frequent GMP, third-party and internal facility inspections to ensure that our manufactured injectable treatments exceed the stringent requirements of importing countries and our distributors.
As a renown Atropine manufacturer and global supplier of 120+ pharmaceutical injection products, our global reach extends to over 65 markets ensuring that pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs and government institutions receive the quality-assured treatments they need.
Uses
What is Atropine used for?
It is used before anesthesia to decrease saliva and other mucus secretions. It is also used as an emergency treatment for slow heartbeats, nerve gas poisoning, and mushroom poisoning.
How are Atropine Injections Used?
This medication is manufactured as a solution that should be administered into the muscle or vein.
What dose should be given?
The usual dose for adults is 0.4-0.6mg.
The usual dose for children is from 0.1-0.6mg, depending on weight.
Refer to a doctor or pharmacist for guidelines on dosage. Do not exceed what they advise.
Can Atropine be used during pregnancy?
Yes, Atropine Injections can be used during pregnancy because there is no adequate data that proves the negative effects of it. It crosses the placental barrier and enters the fetal circulation, but with proper dosage and guidance from doctors, it can be used. It is also unknown if this drug can affect the reproduction capacity.
Can Atropine be used during breastfeeding in women?
It is unknown whether this drug can lead to some serious side effects. However, it has been reported to be excreted in human milk. There is no data if this drug has negative developmental effects during breastfeeding.
Can Atropine be used in geriatric patients?
Yes, Atropine can be used in geriatric patients, but it should be used with caution because older patients are at greater risk of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function. Doses should be carefully adjusted in patients with chronic diseases.
Can Atropine be used in the pediatric population?
Yes, but dosing in pediatric populations has not been well studied.
Are there any dosage recommendations for Atropine?
This drug should be given only when needed. In cases of anesthesia, it is given to decrease saliva and other mucus secretions. It is also given for the treatment of slow heartbeats, nerve gas poisoning, or mushroom poisoning. In cases of poisoning, it should be given only in situations where the exposure is known or suspected. Patients should get proper dosage depending on their health status, and they should be monitored for at least 48 to 72 hours.
What happens in cases of Atropine overdose?
Excessive administration may result in palpitations, dilated pupils, difficulty swallowing, hot dry skin, thirst, dizziness, restlessness, tremors, fatigue, and ataxia. Toxic doses can induce heightened restlessness, excitement, hallucinations, delirium, and coma. Severe intoxication may lead to depression, circulatory collapse, reduced blood pressure, respiratory failure, paralysis, and ultimately death.
In pediatric populations, high doses of Atropine might lead to fatal outcomes. In cases of toxic overdose, a short-acting barbiturate or diazepam can be administered as needed to manage pronounced excitement and convulsions. Caution is advised against large sedative doses to avoid potential overlap with the depressive effects seen in later stages of atropine poisoning. Central stimulants are not recommended. Physostigmine is an atropine antidote that can be given intravenously to pediatric populations. It alleviates delirium and coma resulting from significant atropine doses. Due to rapid physostigmine breakdown, the patient may relapse into a coma after one to two hours, necessitating repeated doses.
Artificial respiration with oxygen may be essential in severe cases of overdose, and measures such as ice bags and alcohol sponges can help manage fever, particularly in pediatric populations. This drug is not eliminated by dialysis.
Other warnings
When Atropine is needed for patients with coronary artery disease, the dose should be reduced to avoid the detrimental effects of atropine-induced tachycardia on myocardial oxygen demand.
This drug can precipitate acute glaucoma.
Atropine can lead from partial organic pyloric stenosis to complete obstruction.
Complete urinary retention is a side effect in patients with prostatic hypertrophy.
This drug can lead to the inspissation of bronchial secretions and the formation of viscid plugs in patients with chronic lung disease.
In children under two years and the elderly (>65 years old), the elimination half-life of atropine is more than twice as long compared to other age groups. Gender does not exert any notable effect on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (specifically heart rate changes) of atropine.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Atropine Injection.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- blurred vision
- constipation
- decreased sweating
- dry mouth or throat
- restlessness
- itchiness
- upset stomach
Serious side effects may include:
- signs of an allergic reaction
- changes in heartbeat
- severe skin rash
- increased thirst
- problems with balance or walking; tremors
- changes in vision
Most of the Atropine side effects are due to the antimuscarinic action which leads to dryness of mouth, blurred vision, tachycardia, and photophobia. Heat intolerance might occur in cases of anhidrosis. In older patients, constipation and difficulty in micturition are common.
Hypersensitivity reactions include skin rashes and might progress to exfoliation.
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or you notice any other symptoms, please call your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Atropine Injection if:
- You are allergic to atropine or any of the inactive ingredients.
- You have prostate or digestion problems.
- You have glaucoma, asthma, or tachycardia.
Before treatment, consult your doctor regarding any medications you are taking to address potential drug interactions.
Atropine Injections should be dosed with caution in patients with hepatic or renal impairments.
It should be used with caution in cases of autonomic neuropathy, myocardial ischemia, paralytic ileus, heart failure, hepatic impairment, hiatal hernia with esophagitis reflux, myasthenia gravis, hyperthyroidism, and renal impairment.
It might lead to sweating in warm temperatures or, in cases of excessive exercise, can lead to hyperthermia or heat injury.
This medication should be properly dosed because higher dosages might lead to psychosis.
This drug can cause acute glaucoma. When administered in risky cases, intraocular pressure should be observed.
Patients with pyloric stenosis should be carefully observed for gastrointestinal symptoms.
This drug can cause urinary retention, and it should be given with caution in patients with bladder obstructions.
This medicine can lead to bronchial secretion thickening, and the respiratory status should be observed.
Patients with previous anaphylactic reactions should be carefully observed.
Atropine should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular diseases.
This medication may not be suitable for people with certain conditions, so it is important to consult with a doctor if you have any health conditions.
References
Use of atropine in patients with acute myocardial infarction and sinus bradycardia
This study included 56 patients with acute myocardial infarction that was complicated by sinus bradycardia (SB) and these patients were treated with atropine.
This drug led to decreased or completely abolished premature ventricular contractions and/or bouts of accelerated idioventricular rhythm in 27 of 31 patients (87%). The systemic blood pressure returned to normal in 15 of 17 treated patients (88%) with hypotension.
The conclusion of this study is that atropine can be used for the management of SB and hypotension, as well as effectively treating ventricular arrhythmias.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.